
NIMH » Depression Mood disorder definition is - any of several psychological disorders (such as major depressive disorder or bipolar disorder) characterized by abnormalities of emotional state —called also affective disorder.
The Mood Disorder Questionnaire (MDQ) Overview
Mood Disorders List of High Impact Articles PPts. Demi Lovato shares her personal story with mental health problems and offers advice for young adults. If you have, or believe you may have, a mental health problem, it …, Mood disorders are a category of illnesses that describe a serious change in mood. Illness under mood disorders include: major depressive disorder, bipolar disorder (mania - euphoric, hyperactive, over inflated ego, unrealistic optimism), persistent depressive disorder (long lasting low grade depression), cyclothymia (a mild form of bipolar disorder), and SAD (seasonal affective disorder)..
The Mood Disorder Questionnaire (MDQ) was developed by a team of psychiatrists, researchers and consumer advocates to address the need for timely and accurate evaluation of bipolar disorder. Clinical Utility n The MDQ is a brief self-report instrument that takes about 5 minutes to complete. Mood disorders appear to have a genetic component, with genetic factors playing a more prominent role in bipolar disorder than in depression. Both biological and psychological factors are important in the development of depression. People who suffer from mental health problems, especially mood disorders, are at heightened risk for suicide.
About Mood Disorders. Marked by changes in mood, depression and bipolar disorder (also known as manic depression) are both highly treatable, medical illnesses. Unfortunately, many people don't get the help they need because of the misunderstanding surrounding … able to identify seven out of ten people who have bipolar disorder and screen out nine out of ten people who do not.1 A recent National DMDA survey revealed that nearly 70% of people with bipolar disorder had received at least one misdiagnosis and many had waited more than 10 years from the onset of their symptoms before receiving a correct
Mood disorders that go undiagnosed can put kids at risk for other conditions, like disruptive behavior and substance use disorders, that remain after the mood disorder is treated. Children and teens with a mood disorder don’t always show the same symptoms as adults. Mood disorder is a broad term that's used to include all the different types of depression and bipolar disorder, both of which affect your mood. If you have symptoms of a mood disorder, your moods may range from extremely low ( depressed) to extremely high or irritable (manic).
Bipolar mood disorder is a form of depressive disorder that used to be called manic depressive illness. People with bipolar mood disorder experience extreme mood swings - from depression and sadness to elation and excitement. The mood swings tend to The Mood Disorder Questionnaire (MDQ) was developed by a team of psychiatrists, researchers and consumer advocates to address the need for timely and accurate evaluation of bipolar disorder. Clinical Utility n The MDQ is a brief self-report instrument that takes about 5 minutes to complete.
Mood Disorders Emotional extremes of mood disorders come in two principal forms. 1. Major depressive disorder 2. Bipolar disorder 39 Major Depressive Disorder In terms of frequency, depression is the “common cold” of psychological disorders. In a year, 5.8% of men and 9.5% of women report depression worldwide (WHO, 2002). Mood disorder definition is - any of several psychological disorders (such as major depressive disorder or bipolar disorder) characterized by abnormalities of emotional state —called also affective disorder.
mood disorders mental disorders whose essential feature is a disturbance of mood manifested by episodes of manic, hypomanic, or depressive symptoms, or some combination of these. The two major categories are bipolar disorders and depressive disorders . Mood disorder not otherwise specified is more commonly known as Mood Disorder NOS. Mood Disorder NOS is a general term for any mood disorder that isn’t included under its own term in the DSM-IV. “NOS” is merely “not otherwise specified” abbreviated. The DSM-IV is the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders.
DSM-5 and Psychotic and Mood Disorders George F. Parker, MD The criteria for the major psychotic disorders and mood disorders are largely unchanged in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5), with a few important exceptions: a new assessment Bipolar Disorder. Bipolar disorder (previously called manic depression) is a mood disorder in which a person experiences periods of depression, periods of elevated moods (whether elated or irritable) and increased energy, periods of no symptoms, and – for some – mixed states with symptoms of depression and symptoms of mania simultaneously. These mood cycles can last for as short as hours
A mood disorder is a mental health class that health professionals use to broadly describe all types of depression and bipolar disorders. Children, teens, and adults can have mood disorders. However, children and teens don’t always have the same symptoms as adults. mood disorder n. Any of a group of psychiatric disorders, including depression and bipolar disorder, characterized by a pervasive disturbance of mood. Also called affective disorder. Affective Disorder A condition marked by changes in affect (mood/emotion), which is not attributable to organic (physical) disease. Examples Major depressive disorder
markedly labile mood, reckless or aggressive behav-iors, or psychotic symptoms may be experiencing the initial symptoms of a bipolar disorder. MOOD DISORDERS KEY FACTS The prevalence of mood disorders in children and adolescents ages 9–17 years is approximately 6 percent (U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, 1999). markedly labile mood, reckless or aggressive behav-iors, or psychotic symptoms may be experiencing the initial symptoms of a bipolar disorder. MOOD DISORDERS KEY FACTS The prevalence of mood disorders in children and adolescents ages 9–17 years is approximately 6 percent (U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, 1999).
markedly labile mood, reckless or aggressive behav-iors, or psychotic symptoms may be experiencing the initial symptoms of a bipolar disorder. MOOD DISORDERS KEY FACTS The prevalence of mood disorders in children and adolescents ages 9–17 years is approximately 6 percent (U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, 1999). Bipolar Disorder. Bipolar disorder (previously called manic depression) is a mood disorder in which a person experiences periods of depression, periods of elevated moods (whether elated or irritable) and increased energy, periods of no symptoms, and – for some – mixed states with symptoms of depression and symptoms of mania simultaneously. These mood cycles can last for as short as hours
THE MOOD DISORDER QUESTIONNAIRE. Mood disorders appear to have a genetic component, with genetic factors playing a more prominent role in bipolar disorder than in depression. Both biological and psychological factors are important in the development of depression. People who suffer from mental health problems, especially mood disorders, are at heightened risk for suicide., Disruptive Mood Dysregulation Disorder (DMDD) is a relatively new diagnosis in the field of mental health. Children with DMDD have severe and frequent temper tantrums that interfere with their ability to function at home, in school or with their friends. Some of these children were previously diagnosed with bipolar disorder, even though they often.
Defining and Understanding Mood Disorders Video & Lesson

Mood disorder Wikipedia. 14.6 MOOD DISORDERS: CLINICAL FEATURES HAGOP S. AKISKAL, M.D. Heterogeneity of Mood Disorders Affects, Moods, Temperaments, and Morbid Mood States Psychopathology Diagnostic Classification Depressive Disorders Bipolar Disorders Mood Disorders not otherwise Specified Differential Diagnosis ICD-10 Suggested Cross-References, What is a personality disorder? Everyone has personality traits that characterise them. These are the usual ways that a person thinks and behaves, which make each of us unique. Personality traits become a personality disorder when the pattern of thinking and behaviour is ….

What is a Mood Disorder? – Families for Depression Awareness

Psychological Disorders Purdue. Mood Disorders Mood disorders is a psychological disorder characterized by the elevation or lowering of a person's mood, such as depression or bipolar disorder. A mood disorder is a group of diagnoses in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders classification system where a disturbance in the person's mood is hypothesized to be https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Depression Nov 01, 2019 · These include depression and bipolar disorder (also called manic depression). Mood disorders can increase a person's risk for heart disease, diabetes, and other diseases. Treatments include medication, psychotherapy, or a combination of both. With treatment, most people with mood disorders can lead productive lives..

What is bipolar mood disorder? Bipolar mood disorder is a form of depressive disorder that used to be called manic depressive illness. People with bipolar mood disorder experience extreme mood swings - from depression and sadness to elation and excitement. The mood swings tend to recur, can vary from mild to severe, and can be of different There are also two main views of what causes mood disorders: the biological view, which says that mood disorders are caused by chemical imbalances in the brain, and the psychosocial view, which
Learn about Mood Disorders on Healthgrades.com, including information on symptoms, causes and treatments. Learn about Mood Disorders on Healthgrades.com, including information on symptoms, causes and treatments. Skip navigation. Search. Near. Cancel Search. Find a doctor Back Find a Doctor. Find doctors by specialty Nov 01, 2019 · These include depression and bipolar disorder (also called manic depression). Mood disorders can increase a person's risk for heart disease, diabetes, and other diseases. Treatments include medication, psychotherapy, or a combination of both. With treatment, most people with mood disorders can lead productive lives.
About Mood Disorders. Marked by changes in mood, depression and bipolar disorder (also known as manic depression) are both highly treatable, medical illnesses. Unfortunately, many people don't get the help they need because of the misunderstanding surrounding … Disruptive Mood Dysregulation Disorder (DMDD) is a relatively new diagnosis in the field of mental health. Children with DMDD have severe and frequent temper tantrums that interfere with their ability to function at home, in school or with their friends. Some of these children were previously diagnosed with bipolar disorder, even though they often
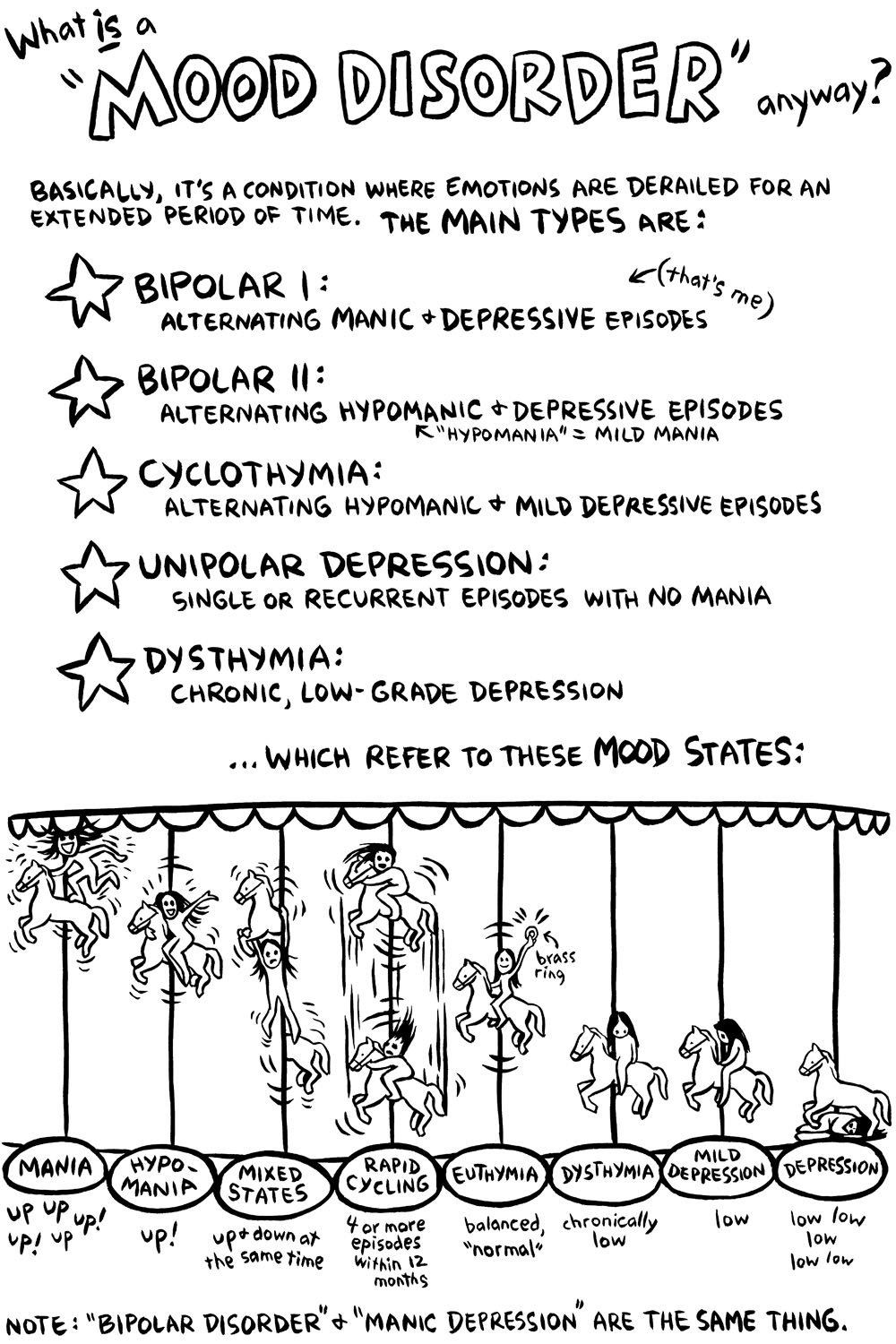
Disruptive Mood Dysregulation Disorder (DMDD) is a relatively new diagnosis in the field of mental health. Children with DMDD have severe and frequent temper tantrums that interfere with their ability to function at home, in school or with their friends. Some of these children were previously diagnosed with bipolar disorder, even though they often it's a condition where emotions are Þerau-ed for an extended the main types bipolar : manic +depresqve episodes mania depressive or recurrent no mania
The Mood Disorder Questionnaire (MDQ) was developed by a team of psychiatrists, researchers and consumer advocates to address the need for timely and accurate evaluation of bipolar disorder. Clinical Utility n The MDQ is a brief self-report instrument that takes about 5 minutes to complete. DSM-5 and Psychotic and Mood Disorders George F. Parker, MD The criteria for the major psychotic disorders and mood disorders are largely unchanged in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5), with a few important exceptions: a new assessment
Bipolar Disorder. Bipolar disorder (previously called manic depression) is a mood disorder in which a person experiences periods of depression, periods of elevated moods (whether elated or irritable) and increased energy, periods of no symptoms, and – for some – mixed states with symptoms of depression and symptoms of mania simultaneously. These mood cycles can last for as short as hours Mood disorders appear to have a genetic component, with genetic factors playing a more prominent role in bipolar disorder than in depression. Both biological and psychological factors are important in the development of depression. People who suffer from mental health problems, especially mood disorders, are at heightened risk for suicide.
Mood disorder not otherwise specified is more commonly known as Mood Disorder NOS. Mood Disorder NOS is a general term for any mood disorder that isn’t included under its own term in the DSM-IV. “NOS” is merely “not otherwise specified” abbreviated. The DSM-IV is the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. Mood disorder is a broad term that's used to include all the different types of depression and bipolar disorder, both of which affect your mood. If you have symptoms of a mood disorder, your moods may range from extremely low ( depressed) to extremely high or irritable (manic).
There are also two main views of what causes mood disorders: the biological view, which says that mood disorders are caused by chemical imbalances in the brain, and the psychosocial view, which Demi Lovato shares her personal story with mental health problems and offers advice for young adults. If you have, or believe you may have, a mental health problem, it …
Apr 23, 2018 · Affective disorders are a type of psychiatric disorder, or mood disorder, with a broad range of disruptive symptoms. Effective treatments are available, however. We’ll discuss the three main DSM-5 and Psychotic and Mood Disorders George F. Parker, MD The criteria for the major psychotic disorders and mood disorders are largely unchanged in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5), with a few important exceptions: a new assessment
Apr 27, 2015 · 6 Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Techniques for Bipolar Disorder. Keeping your mood stable is key to living well with bipolar disorder. Find out how cognitive behavioral therapy can help. There are also two main views of what causes mood disorders: the biological view, which says that mood disorders are caused by chemical imbalances in the brain, and the psychosocial view, which

Demi Lovato shares her personal story with mental health problems and offers advice for young adults. If you have, or believe you may have, a mental health problem, it … Mood Disorders Mood disorders is a psychological disorder characterized by the elevation or lowering of a person's mood, such as depression or bipolar disorder. A mood disorder is a group of diagnoses in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders classification system where a disturbance in the person's mood is hypothesized to be
Mood disorders AssociAtion of British coluMBiA
Understanding bipolar disorder understanding. Mood disorders/mental illnesses are believed by researchers to be caused by complex imbalances in the brain's chemical activity. Two of the most common mood disorders are depression and bipolar disorder, also known as manic-depressive illness., There are also two main views of what causes mood disorders: the biological view, which says that mood disorders are caused by chemical imbalances in the brain, and the psychosocial view, which.
What is Mood Disorder NOS? AHealthBlog
HANDOUT – MOOD DISORDERS. it's a condition where emotions are Þerau-ed for an extended the main types bipolar : manic +depresqve episodes mania depressive or recurrent no mania, The Mood Disorder Questionnaire (MDQ) was developed by a team of psychiatrists, researchers and consumer advocates to address the need for timely and accurate evaluation of bipolar disorder. Clinical Utility n The MDQ is a brief self-report instrument that takes about 5 minutes to complete..
Mood Disorders Emotional extremes of mood disorders come in two principal forms. 1. Major depressive disorder 2. Bipolar disorder 39 Major Depressive Disorder In terms of frequency, depression is the “common cold” of psychological disorders. In a year, 5.8% of men and 9.5% of women report depression worldwide (WHO, 2002). 1 Introduction The term “mood disorder” refers to a category that includes the following mental health issues: Anxiety Disorders Depression Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) Panic Disorders Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) If you or someone you love has been suffering with a mood disorder, then you are well aware
14.6 MOOD DISORDERS: CLINICAL FEATURES HAGOP S. AKISKAL, M.D. Heterogeneity of Mood Disorders Affects, Moods, Temperaments, and Morbid Mood States Psychopathology Diagnostic Classification Depressive Disorders Bipolar Disorders Mood Disorders not otherwise Specified Differential Diagnosis ICD-10 Suggested Cross-References Feb 28, 2017 · Substance induce mood disorder and mood disorder 2ry to medical condition are the essential differential diagnosis: -Endocrine disorders -Neurological conditions -Systemic disorders -Drugs -Recreational drugs 26. 1. Brain Structure and Functioning 2. Genetics 3. Family History 4. Substance abuse 5. Negative life events 27. 1. Hospitalization. 2.
it's a condition where emotions are Þerau-ed for an extended the main types bipolar : manic +depresqve episodes mania depressive or recurrent no mania Learn about Mood Disorders on Healthgrades.com, including information on symptoms, causes and treatments. Learn about Mood Disorders on Healthgrades.com, including information on symptoms, causes and treatments. Skip navigation. Search. Near. Cancel Search. Find a doctor Back Find a Doctor. Find doctors by specialty
Nov 01, 2019 · These include depression and bipolar disorder (also called manic depression). Mood disorders can increase a person's risk for heart disease, diabetes, and other diseases. Treatments include medication, psychotherapy, or a combination of both. With treatment, most people with mood disorders can lead productive lives. DSM-5 and Psychotic and Mood Disorders George F. Parker, MD The criteria for the major psychotic disorders and mood disorders are largely unchanged in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5), with a few important exceptions: a new assessment
14.6 MOOD DISORDERS: CLINICAL FEATURES HAGOP S. AKISKAL, M.D. Heterogeneity of Mood Disorders Affects, Moods, Temperaments, and Morbid Mood States Psychopathology Diagnostic Classification Depressive Disorders Bipolar Disorders Mood Disorders not otherwise Specified Differential Diagnosis ICD-10 Suggested Cross-References Mood disorders/mental illnesses are believed by researchers to be caused by complex imbalances in the brain's chemical activity. Two of the most common mood disorders are depression and bipolar disorder, also known as manic-depressive illness.
One possibility is that anxiety and mood disorders could be diagnosed on three levels. Rather than separating certain anxiety and mood disorders or all anxiety and mood disorders from each other, specific diagnoses of “emotional disorders” could be given at … mood states. Everyone has variations in their mood, but in bipolar disorder these changes can be very distressing and have a big impact on your life. You may feel that your high and low moods are extreme, and that swings in your mood are overwhelming. Depending on the way you experience these mood …
Mood disorders are a category of illnesses that describe a serious change in mood. Illness under mood disorders include: major depressive disorder, bipolar disorder (mania - euphoric, hyperactive, over inflated ego, unrealistic optimism), persistent depressive disorder (long lasting low grade depression), cyclothymia (a mild form of bipolar disorder), and SAD (seasonal affective disorder). DSM-5 and Psychotic and Mood Disorders George F. Parker, MD The criteria for the major psychotic disorders and mood disorders are largely unchanged in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5), with a few important exceptions: a new assessment
Apr 23, 2018 · Affective disorders are a type of psychiatric disorder, or mood disorder, with a broad range of disruptive symptoms. Effective treatments are available, however. We’ll discuss the three main Mood disorder definition is - any of several psychological disorders (such as major depressive disorder or bipolar disorder) characterized by abnormalities of emotional state —called also affective disorder.
The Mood Disorder Questionnaire (MDQ) was developed by a team of psychiatrists, researchers and consumer advocates to address the need for timely and accurate evaluation of bipolar disorder. Clinical Utility n The MDQ is a brief self-report instrument that takes about 5 minutes to complete. Mood disorders fall into the basic groups of elevated mood, such as mania or hypomania; depressed mood, of which the best-known and most researched is major depressive disorder (MDD) (commonly called clinical depression, unipolar depression, or major depression); and moods which cycle between mania and depression,...
Table 3.19, DSM-IV to DSM-5 Adjustment Disorders Comparison - Impact of the DSM-IV to DSM-5 Changes on the National Survey on Drug Use and Health Your browsing activity is empty. Activity recording is turned off. What is bipolar mood disorder? Bipolar mood disorder is a form of depressive disorder that used to be called manic depressive illness. People with bipolar mood disorder experience extreme mood swings - from depression and sadness to elation and excitement. The mood swings tend to recur, can vary from mild to severe, and can be of different
Mood disorders are a category of illnesses that describe a serious change in mood. Illness under mood disorders include: major depressive disorder, bipolar disorder (mania - euphoric, hyperactive, over inflated ego, unrealistic optimism), persistent depressive disorder (long lasting low grade depression), cyclothymia (a mild form of bipolar disorder), and SAD (seasonal affective disorder). Apr 23, 2018 · Affective disorders are a type of psychiatric disorder, or mood disorder, with a broad range of disruptive symptoms. Effective treatments are available, however. We’ll discuss the three main
Mood Disorders MentalHealth.gov
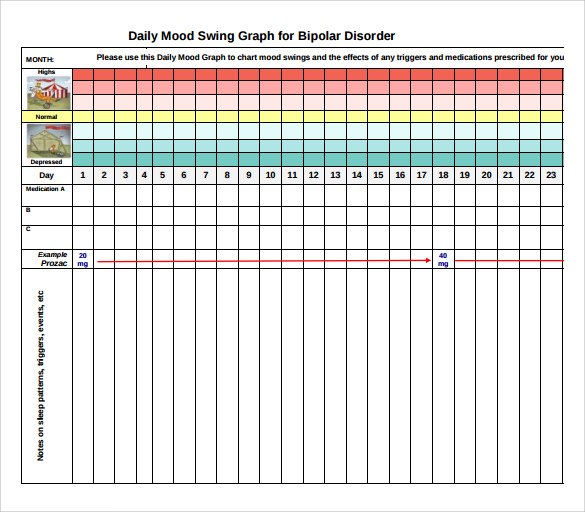
The Various Types of Mood Disorders. Bipolar mood disorder is a form of depressive disorder that used to be called manic depressive illness. People with bipolar mood disorder experience extreme mood swings - from depression and sadness to elation and excitement. The mood swings tend to, mood states. Everyone has variations in their mood, but in bipolar disorder these changes can be very distressing and have a big impact on your life. You may feel that your high and low moods are extreme, and that swings in your mood are overwhelming. Depending on the way you experience these mood ….
Psychological Disorders Purdue. There are also two main views of what causes mood disorders: the biological view, which says that mood disorders are caused by chemical imbalances in the brain, and the psychosocial view, which, There are also two main views of what causes mood disorders: the biological view, which says that mood disorders are caused by chemical imbalances in the brain, and the psychosocial view, which.
Mood disorders slide SlideShare

What is Bipolar mood disorder Department of Health. Table 3.19, DSM-IV to DSM-5 Adjustment Disorders Comparison - Impact of the DSM-IV to DSM-5 Changes on the National Survey on Drug Use and Health Your browsing activity is empty. Activity recording is turned off. https://simple.wikipedia.org/wiki/Depression_(mental_illness) Disruptive Mood Dysregulation Disorder (DMDD) is a relatively new diagnosis in the field of mental health. Children with DMDD have severe and frequent temper tantrums that interfere with their ability to function at home, in school or with their friends. Some of these children were previously diagnosed with bipolar disorder, even though they often.
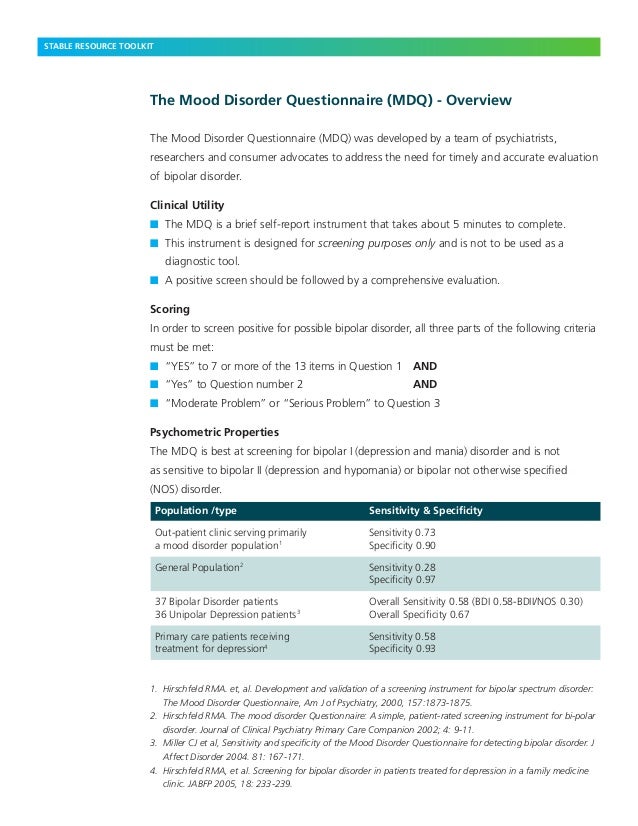
able to identify seven out of ten people who have bipolar disorder and screen out nine out of ten people who do not.1 A recent National DMDA survey revealed that nearly 70% of people with bipolar disorder had received at least one misdiagnosis and many had waited more than 10 years from the onset of their symptoms before receiving a correct Mood Disorders. Mood disorder is the term designated to a set of diagnoses in the American Psychiatric Association (APA) Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, fourth edition (DSM-IV) classification system in which disturbance in a person's mood is …
Apr 23, 2018 · Affective disorders are a type of psychiatric disorder, or mood disorder, with a broad range of disruptive symptoms. Effective treatments are available, however. We’ll discuss the three main Mood disorders AssociAtion of British coluMBiA Bipolar disorder is a class of mood disorders that is marked by dramatic changes in mood, energy and behaviour. The key characteristic is that people with bipolar disorder alternate be-tween episodes of mania (extreme elevated mood) and …
Mood disorders AssociAtion of British coluMBiA Bipolar disorder is a class of mood disorders that is marked by dramatic changes in mood, energy and behaviour. The key characteristic is that people with bipolar disorder alternate be-tween episodes of mania (extreme elevated mood) and … Mood disorder definition is - any of several psychological disorders (such as major depressive disorder or bipolar disorder) characterized by abnormalities of emotional state —called also affective disorder.
Mood disorders fall into the basic groups of elevated mood, such as mania or hypomania; depressed mood, of which the best-known and most researched is major depressive disorder (MDD) (commonly called clinical depression, unipolar depression, or major depression); and moods which cycle between mania and depression,... Mood Disorders Emotional extremes of mood disorders come in two principal forms. 1. Major depressive disorder 2. Bipolar disorder 39 Major Depressive Disorder In terms of frequency, depression is the “common cold” of psychological disorders. In a year, 5.8% of men and 9.5% of women report depression worldwide (WHO, 2002).
The DSM-5, scheduled for publication in 2013, will be the latest version of the American Psychiatric Association's Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders.Note: This chart lists major disorders only and is not meant to be comprehesive. One possibility is that anxiety and mood disorders could be diagnosed on three levels. Rather than separating certain anxiety and mood disorders or all anxiety and mood disorders from each other, specific diagnoses of “emotional disorders” could be given at …
Mood disorders fall into the basic groups of elevated mood, such as mania or hypomania; depressed mood, of which the best-known and most researched is major depressive disorder (MDD) (commonly called clinical depression, unipolar depression, or major depression); and moods which cycle between mania and depression,... Feb 28, 2017 · Substance induce mood disorder and mood disorder 2ry to medical condition are the essential differential diagnosis: -Endocrine disorders -Neurological conditions -Systemic disorders -Drugs -Recreational drugs 26. 1. Brain Structure and Functioning 2. Genetics 3. Family History 4. Substance abuse 5. Negative life events 27. 1. Hospitalization. 2.
Mood disorders/mental illnesses are believed by researchers to be caused by complex imbalances in the brain's chemical activity. Two of the most common mood disorders are depression and bipolar disorder, also known as manic-depressive illness. it's a condition where emotions are Þerau-ed for an extended the main types bipolar : manic +depresqve episodes mania depressive or recurrent no mania
Mood Disorders. Mood disorder is the term designated to a set of diagnoses in the American Psychiatric Association (APA) Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, fourth edition (DSM-IV) classification system in which disturbance in a person's mood is … Disruptive Mood Dysregulation Disorder (DMDD) is a relatively new diagnosis in the field of mental health. Children with DMDD have severe and frequent temper tantrums that interfere with their ability to function at home, in school or with their friends. Some of these children were previously diagnosed with bipolar disorder, even though they often
What is bipolar mood disorder? Bipolar mood disorder is a form of depressive disorder that used to be called manic depressive illness. People with bipolar mood disorder experience extreme mood swings - from depression and sadness to elation and excitement. The mood swings tend to recur, can vary from mild to severe, and can be of different 14.6 MOOD DISORDERS: CLINICAL FEATURES HAGOP S. AKISKAL, M.D. Heterogeneity of Mood Disorders Affects, Moods, Temperaments, and Morbid Mood States Psychopathology Diagnostic Classification Depressive Disorders Bipolar Disorders Mood Disorders not otherwise Specified Differential Diagnosis ICD-10 Suggested Cross-References
The DSM-5, scheduled for publication in 2013, will be the latest version of the American Psychiatric Association's Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders.Note: This chart lists major disorders only and is not meant to be comprehesive. mood disorders mental disorders whose essential feature is a disturbance of mood manifested by episodes of manic, hypomanic, or depressive symptoms, or some combination of these. The two major categories are bipolar disorders and depressive disorders .
Mood Disorders Emotional extremes of mood disorders come in two principal forms. 1. Major depressive disorder 2. Bipolar disorder 39 Major Depressive Disorder In terms of frequency, depression is the “common cold” of psychological disorders. In a year, 5.8% of men and 9.5% of women report depression worldwide (WHO, 2002). Apr 27, 2015 · 6 Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Techniques for Bipolar Disorder. Keeping your mood stable is key to living well with bipolar disorder. Find out how cognitive behavioral therapy can help.


